Beta – A metric that relatively measures sensitivity to market movements over a specified period of time. The beta of the market is equal to 1; a beta higher than 1 implies that a return was more volatile than the market. A beta lower than 1 suggests that a return was less volatile than the market
Developed market – An economy with a relatively high level of economic growth, standard of living, income or gross domestic product (GDP) per capita and infrastructure.
Emerging market – An emerging market economy is the economy of a developing nation that is becoming more engaged with global markets as it grows.
Emerging market debt (EMD) – Emerging market debt (EMD) is a term used to describe bonds issued by countries with developing economies as well as by corporations within those nations.
Hard currency – Refers to money issued by a nation that is seen as politically and economically stable. Hard currencies are widely accepted around the world as a form of payment for goods and services and may be preferred over domestic (local) currency.
High yield – A high yield bond is one with a lower credit rating than an investment-grade bond. High-yield bonds typically offer a higher rate of interest because of a greater risk of default. As such, higher yielding, higher risk bonds can fluctuate in price more than investment-grade bonds, so investors should maintain a long-term perspective.
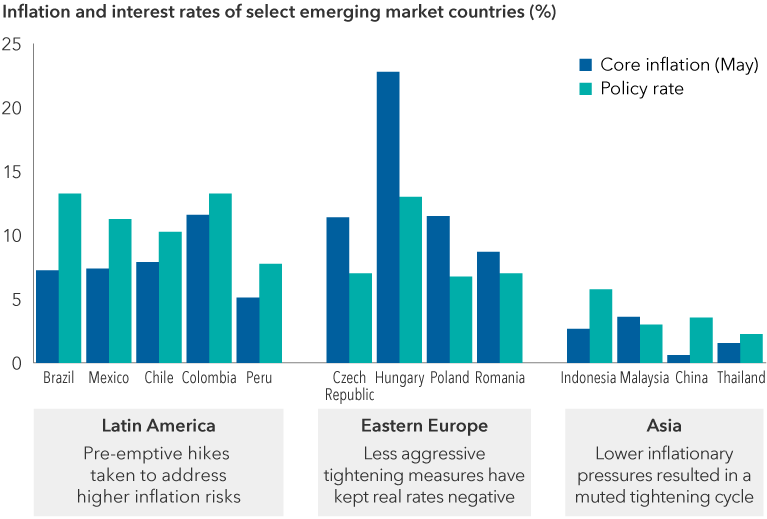
Inflation – The rise in the prices of goods and services, as happens when spending increases relative to the supply of goods on the market – in other words, too much money chasing too few goods. Core inflation metrics strip out volatile items like food and energy.
Investment-grade credits/issues/securities – Assets rated BBB-minus or higher by rating agencies Moody’s, Standard & Poor’s or Fitch.
Issuer – A legal entity that develops, registers and sells securities to finance its operations. Issuers may be corporations, investment trusts, or governments.
Local currency – A currency that can be spent in a particular geographical locality at participating organizations.
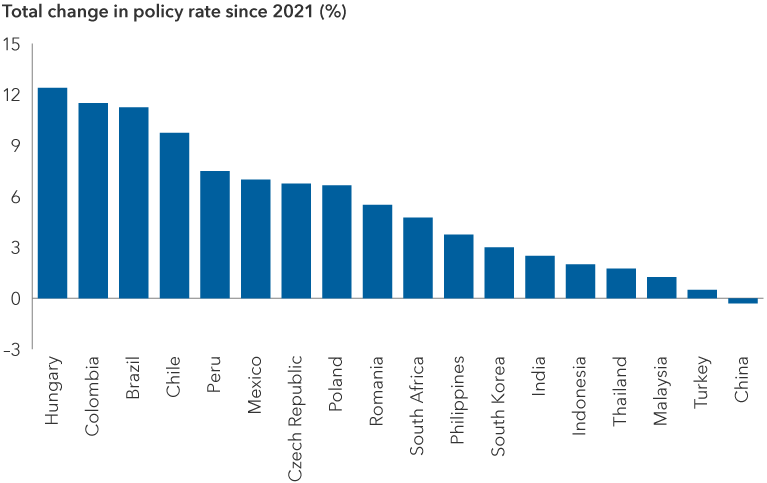
Monetary policy – A set of tools used by a central bank to manage the country’s money supply and promote economic growth. In an economic slowdown, a central bank may adopt an accommodative (expansionary) policy to boost the economy by measures such as lowering interest rates. When inflation is high, a central bank may adopt monetary tightening (contractionary) by increasing interest rates to slow growth and decrease inflation.
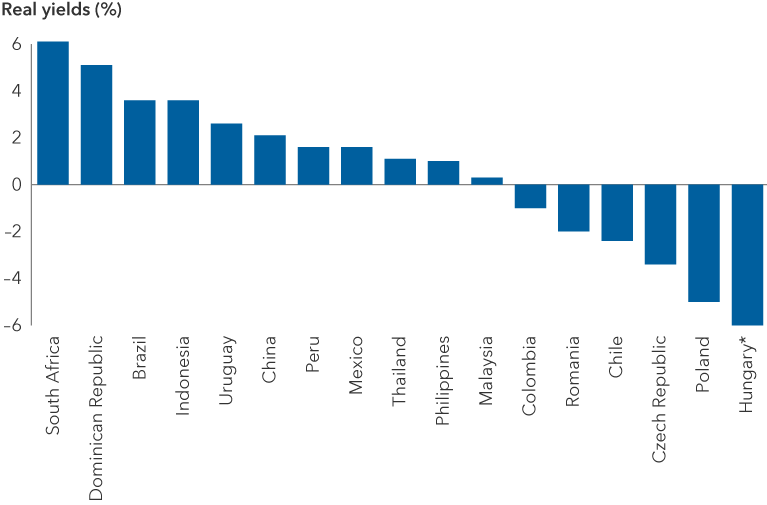
Real interest rate – An interest rate adjusted for inflation.
Sovereign bonds – A debt security issued by a national government.
BLOOMBERG® is a trademark and service mark of Bloomberg Finance L.P. and its affiliates (collectively “Bloomberg”). Bloomberg or Bloomberg’s licensors own all proprietary rights in the Bloomberg Indices. Neither Bloomberg nor Bloomberg’s licensors approves or endorses this material, or guarantees the accuracy or completeness of any information herein, or makes any warranty, express or implied, as to the results to be obtained therefrom and, to the maximum extent allowed by law, neither shall have any liability or responsibility for injury or damages arising in connection therewith.
The J.P. Morgan Emerging Market Bond Index (EMBI) Global Diversified is a uniquely weighted emerging market debt benchmark that tracks total returns for U.S. dollar-denominated bonds issued by emerging market sovereign and quasi-sovereign entities. This index is unmanaged, and its results include reinvested dividends and/or distributions but do not reflect the effect of account fees, expenses or U.S. federal income taxes.
J.P. Morgan Government Bond Index – Emerging Markets Global Diversified covers the universe of regularly traded, liquid fixed-rate, domestic currency emerging market government bonds to which international investors can gain exposure. This index is unmanaged, and its results include reinvested dividends and/or distributions but do not reflect the effect of account fees, expenses or U.S. federal income taxes.