Aerospace
Witnessing an F-35 jet fighter take off vertically as it rapidly achieves speeds beyond the sound barrier and then swiftly returns to earth in a vertical descent is a stunning experience, according to equity portfolio manager Jason Smith.
“I have seen an F-35 take flight a few times,” says Smith, who attended a demonstration in July at the Farnborough International Airshow outside London. “It’s hard not to be awestruck every time.”
Smith, who covers European industrials, airlines, aerospace and defense companies as an analyst, didn’t attend the event simply for the spectacle. He and eight colleagues went to see the latest advancements in commercial aviation, meet with management teams and gain insights into the industry overall.
“Getting out on the road to kick the tires and meeting face-to-face with management are cornerstones of our research process,” says Lara Pellini, an equity portfolio manager based in London who accompanied Smith.
“During the pandemic we managed with virtual meetings, but Farnborough was a great opportunity to harvest and replenish relationships, and take the temperature of the commercial aircraft market,” she explains.
Here, Smith and Pellini identify six key insights from their trip to Farnborough.
1. There’s no substitute for being there
The aerospace and defense industry hosts shows all over the world, but the two most important are held in Farnborough and Paris in alternating years. At these events leading companies gather to meet with customers and investors, announce major business deals and showcase the latest technological advances. The 2022 event featured Airbus and Boeing, engine makers Safran and Rolls-Royce, and defense companies Lockheed Martin, Rheinmetall and BAE Systems — among others.
While much can be discovered by reading industry research, constructing models and learning about addressable markets, it is hard to fully understand whether a plane or helicopter lives up to the hype by watching a video on YouTube.
“There really is no substitute for being there,” says Pellini. “I may already have a point of view but traveling with our investment analysts to see the companies we might invest in, visiting their operations and interacting with management helps crystalize my thinking and provides a better frame of reference going forward.”
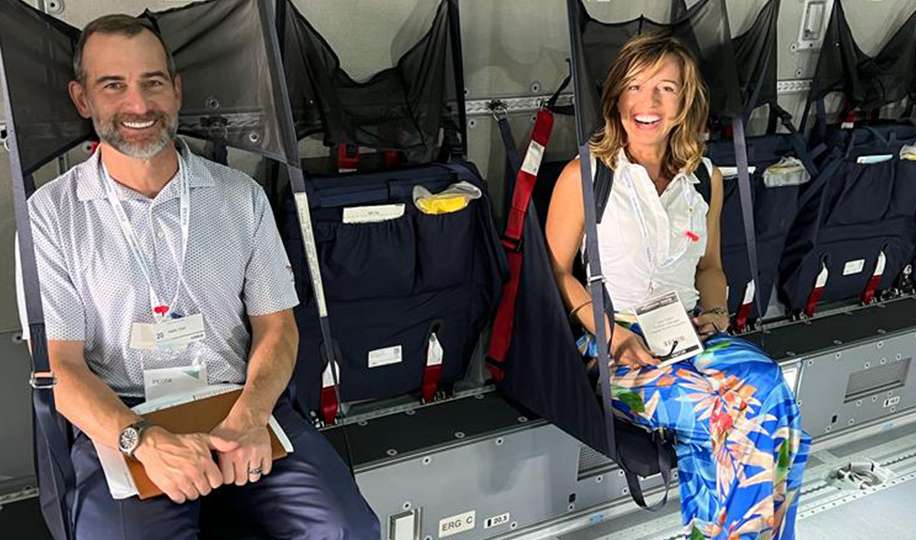

During the show, the portfolio managers and analysts boarded several aircraft, including an Airbus A400M military transport plane. They sat in the cockpit and toured the crew’s sleeping quarters in an A350-900 wide-body jet and had every feature of a H145 helicopter explained in detail.
Day three featured the F-35 demonstration. “When the jet took off, it blasted noise limits,” says Smith. “Before we departed, we also observed the amazing maneuverability of Boeing’s double rotor Chinook helicopter, which performed a series of twists, turns and steep climbs.”
Hands-on experiences can help investors get a better grasp of concepts like fuel efficiency, for example, and track the impact of innovation and disruption over time.
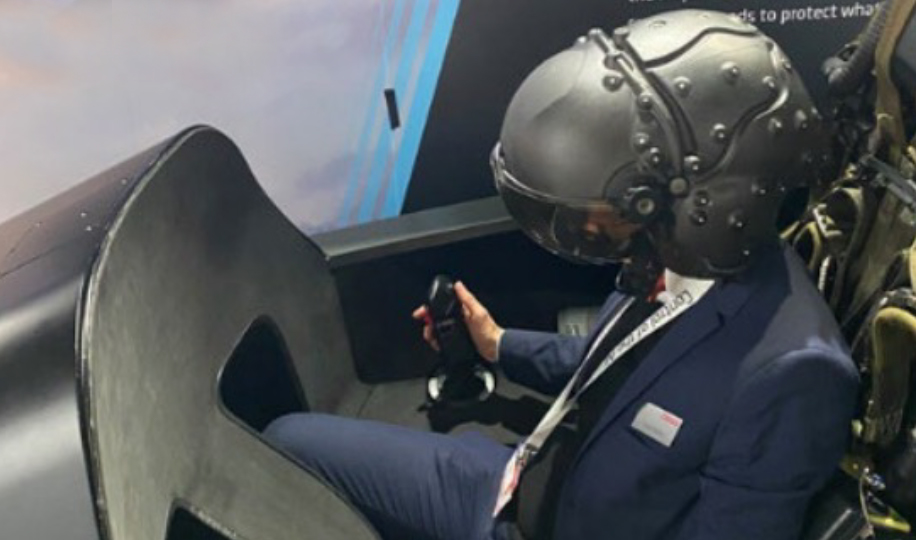
“Simply boarding the plane and witnessing how the cabin is optimized to keep it compact can give you a sense of how fuel efficient a plane might be,” Pellini says. “I also was struck by how much these companies have picked up from the gaming industry. In some new simulation machines, the pilot wears a helmet with a headset and sees only what is in the helmet, much like a virtual reality gaming system.”

2. Air travel is taking off again
In the case of this trip, the simple act of getting there offered anecdotal evidence about the health of global travel. Smith, who is based in New York, said his flight to London was full, the airport was packed and security delays were long. “Anyone who has been in a plane the last few months — and recent data suggests many have been — can appreciate that airfares have probably never been higher.”
This bodes well for the aerospace industry as well as the airlines. After two years of mostly empty skies and a COVID-related freeze on plane orders, the airlines are now scrambling to get planes delivered and replace others with newer, more fuel-efficient models. In fact, the world’s two major aircraft makers, Airbus and Boeing, have order backlogs totaling more than 10.5 years of production.
A long runway for commercial aircraft production
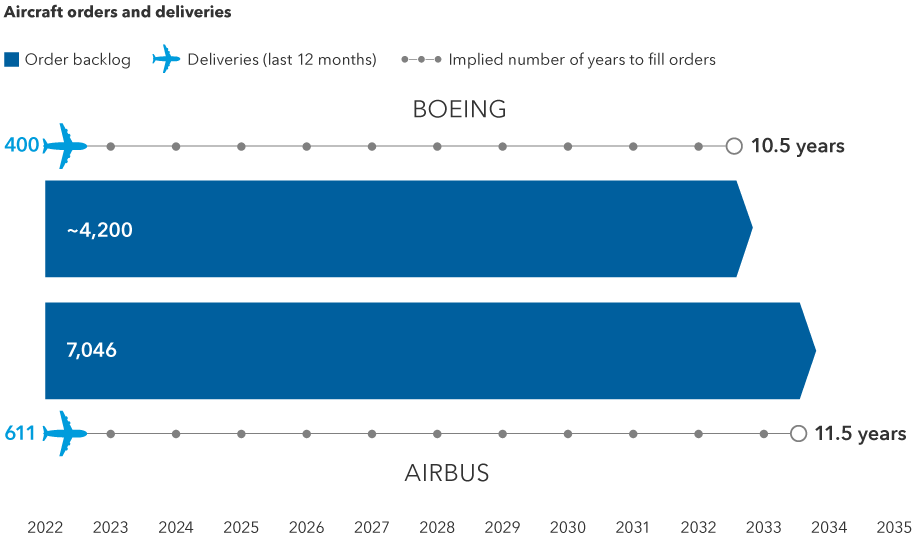
Sources: Capital Group, company reports. Boeing's last reported order backlog is over 4,200, while Airbus has an order backlog of 7,046 planes. As of June 30, 2022.
These numbers were supported by conversations and announcements at the air show. To be sure, the overall tone was somewhat subdued compared to pre-pandemic shows, says Pellini. At times temperatures reached 120 degrees Fahrenheit on the tarmac. Attendance was down and companies hosted fewer meetings. And while the announced orders were lighter than pre-COVID events, a few were significant.
Another key takeaway: “Many people told us they were surprised at how quickly corporate travel has rebounded,” says Smith. “With working from home more accepted or simply necessary, there were fears that we'd be down 20% or 30%. In some markets it’s returned to 2019 levels and in others it’s down only 10% to 15%. That suggests that Zoom fatigue has set in. People want to get out and travel.”
3. Certain companies may benefit from a defense “super-cycle”
One consistent insight that came out of nearly every conversation is that geopolitical tensions are growing, not just in Europe but across the globe. This, of course, has been in news headlines for some time. Indeed, Germany recently disclosed plans to spend 100 billion euros in the next four years on defense, its biggest shift in foreign policy since World War II. Japan indicated it would double its budget.
“Whether in the Pacific or Eastern Europe, a common theme is that the divide between the East and the West has resurfaced and is widening,” Pellini says. “The world is less safe. This is unfortunate, but it does present opportunity for defense contractors. With security now top of mind for politicians, voters and even some investors, I believe we may be at the start of a super-cycle for defense.”
But not all defense companies will benefit, explains Pellini. The key is to understand which specific companies have the most useful innovations, are well positioned to execute on their business plan and can overcome challenges like supply chain disruptions.
Global risks have grown
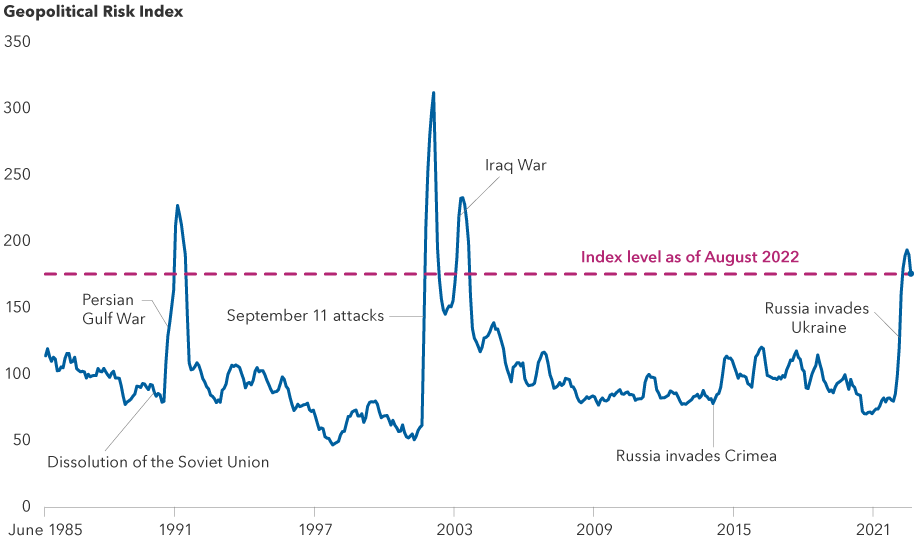
Sources: Capital Group; Caldara, Dario and Matteo Iacoviello (2022), “Measuring Geopolitical Risk,” American Economic Review, April, 112(4), pp.1194-1225. The Geopolitical Risk Index is a measure of adverse geopolitical events and associated risks based upon the tally of newspaper articles covering geopolitical tensions, using a sample of 10 newspapers going back to 1985. Index level values reflect a six-month smoothed average of monthly data. As of August 2022.
4. Face-to-face meetings sharpen the picture
Rising demand for air travel and higher defense spending are well known. What’s not as clear, though, are which companies are best positioned to take advantage of these secular trends. That’s why research trips like this one to Farnborough are so important to build a better understanding of business models, assess company operations and products, and determine whether a management team can execute.
According to Pellini CEOs and CFOs are more willing to share information and offer opinions about competitors when they are speaking directly with you. “It’s easier to ask tough questions and pick up nuances in their tone of voice, as well as non-verbal cues.”
“Once a manager is more relaxed, they often become more engaged and willing to be open about what keeps them up at night or what they’re excited about,” Smith adds.
“There were a number of candid conversations that we came away from with more certainty about the sincerity of a manager’s upbeat forecast or their reports about strengthening demand. This is something you can’t get from a Zoom encounter, and these conversations were very useful in confirming our investment theses.”
While meetings with CEOs and CFOs are important, sometimes the most compelling or useful insights can be gleaned from conversations with line managers and other executives. For example, during a Farnborough meeting, the executive vice president of an engine maker explained how key industry participants are aligning to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
“He really knew his stuff and presented it so well,” says Smith. The executive, whose background is in space and hydrogen, identified three levers his company can use to achieve new emissions standards: burn less fuel, burn better fuel and make everything lighter.
“We spent a lot of time talking about the innovation timelines required to make their target,” adds Smith. “The most fascinating part of the conversation was how this executive was able to explain the complexities of developing hydrogen into a safe, reliable and green fuel source to layman like me.”
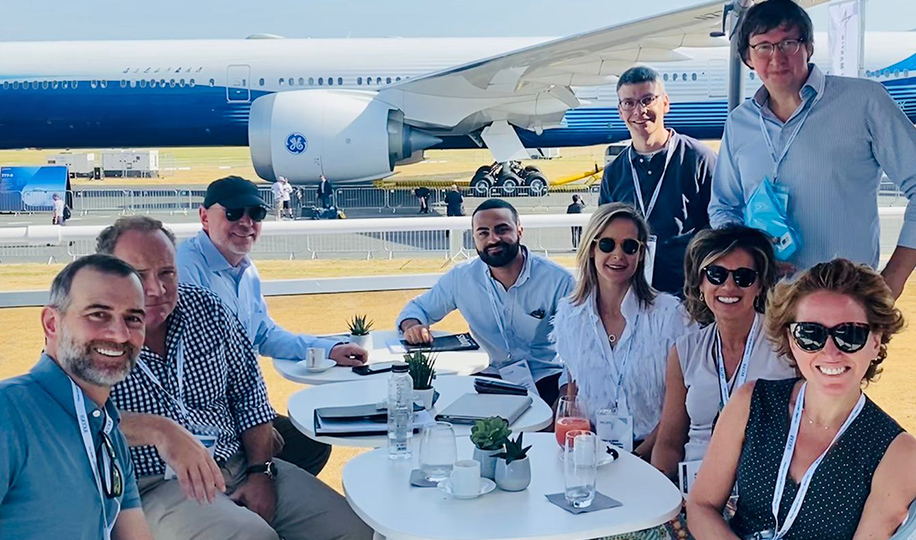

5. The lightbulbs shine in the meeting after the meeting
The bus ride to and from Farnborough and the hotel in London took as much as 90 minutes to two hours depending on traffic. That often was when the light bulbs shined the brightest.
When nine people share a confined space for that much time, they can strategize for upcoming meetings. They might decide what key information they want to get from a particular meeting, key questions to be asked and who should do the asking.
“We used the bus ride back to the hotel as a debriefing period, where we discussed what we liked and didn't like,” says Smith. “The group shared differing perspectives on what they thought were the crucial takeaways. And between the nine of us, we came away with a broad spectrum of answers, views and concerns. So it really is a useful process — and one we've used for years.”
6. Research trips can lead to better investment decisions
Overall, the group came away from Farnborough feeling constructive about several companies in the aerospace and defense industry, even if major economies were to slip into recession in the coming year.
“The pandemic prompted the worst recession in the history of the commercial aircraft industry,” Pellini says. “Today the industry is recovering — and a number of tailwinds are supporting the recovery.”
Before COVID, passenger growth had been resilient to external shocks. In fact, over the last 50 years, the industry has been growing at a compounded annual growth rate of 5%. Airbus, for example, has at least 17 years of consistent aircraft deliveries. After delaying plane deliveries for two years, many airlines today are ordering planes five years out.
“I would argue that the pent-up demand for planes has never been stronger,” Pellini adds.
To be fair, consistent deliveries in past downturns did not prevent share prices from meaningfully falling. The industry faces other challenges, including supply chain constraints and a U.S. labor shortage that's hurting engine manufacturers, which in turn is impacting both Airbus and Boeing.
“Nevertheless, despite the muted tone at the air show, there was also a generally relaxed feeling,” Smith concludes. “Passengers are flying again, airlines are placing orders, and as long as supply chains can improve and companies can continue to meet demand, the outlook for the next three to five years appears positive.”
Indexes are unmanaged and, therefore, have no expenses. Investors cannot invest directly in an index.
Investing outside the United States involves risks, such as currency fluctuations, periods of illiquidity and price volatility, as more fully described in the prospectus. These risks may be heightened in connection with investments in developing countries.
Small-company stocks entail additional risks, and they can fluctuate in price more than larger company stocks.
The return of principal for bond funds and for funds with significant underlying bond holdings is not guaranteed. Fund shares are subject to the same interest rate, inflation and credit risks associated with the underlying bond holdings. Lower rated bonds are subject to greater fluctuations in value and risk of loss of income and principal than higher rated bonds.
MSCI ACWI is a free float-adjusted market capitalization-weighted index that is designed to measure equity market results in the global developed and emerging markets, consisting of more than 40 developed and emerging market country indexes.
MSCI has not approved, reviewed or produced this report, makes no express or implied warranties or representations and is not liable whatsoever for any data in the report. You may not redistribute the MSCI data or use it as a basis for other indices or investment products.
Standard & Poor‘s 500 Composite Index is a market capitalization-weighted index based on the results of approximately 500 widely held common stocks.
Standard & Poor’s 500 Composite Index (“Index”) is a product of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC and/or its affiliates and has been licensed for use by Capital Group. Copyright © 2020 S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, a division of S&P Global, and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Redistribution or reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without written permission of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC.
Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Index represents the U.S. investment-grade fixed-rate bond market.
Bloomberg® is a trademark of Bloomberg Finance L.P. (collectively with its affiliates, “Bloomberg”). Barclays® is a trademark of Barclays Bank Plc (collectively with its affiliates, “Barclays”), used under license. Neither Bloomberg nor Barclays approves or endorses this material, guarantees the accuracy or completeness of any information herein and, to the maximum extent allowed by law, neither shall have any liability or responsibility for injury or damages arising in connection therewith.
©2020 Morningstar, Inc. All rights reserved. The information contained herein: (1) is proprietary to Morningstar and/or its content providers; (2) may not be copied or distributed; and (3) is not warranted to be accurate, complete or timely. Neither Morningstar nor its content providers are responsible for any damages or losses arising from any use of this information. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
 Lara Pellini
Lara Pellini
 Jason Smith
Jason Smith